Power interruptions are among the top causes of IT downtime, equipment failure, and data corruption…
Disaster Recovery Challenges for SMEs in Kenya
Some individuals believe that Disaster Recovery for SMEs is essentially the same as backup. Others adopt a “set it and forget it” approach to both backup and disaster recovery solutions. However, adhering to either of these perspectives can significantly jeopardize corporate data.
Why is this the case?
A robust disaster recovery plan must encompass all facets of recovery, from defining recovery time and recovery point objectives to outlining precise methods for restoring the impacted infrastructure.
Ideally, you should have a comprehensive strategy in place to manage your entire infrastructure during any unexpected event, including a pandemic, to ensure your business remains operational.
In summary, disaster recovery for SMEs is a multifaceted, intricate, and interrelated process. Small to medium-sized businesses cannot afford to overlook this aspect and assume their data is perpetually secure and accessible.
This article will provide an overview of the primary disaster recovery challenges faced by SMEs in Kenya. By addressing these challenges, you can strengthen your disaster recovery strategies and protect valuable data.
Overall Disaster Recovery Complexity
The foremost challenge is the complexity inherent in today’s corporate landscape. Currently, data and workloads are distributed
across various applications, computers, servers, and platforms.
To remain competitive, it is essential to continuously assess and adapt your software and hardware to the evolving environment. Additionally, significant transitions, such as the recent migration from local infrastructures to predominantly cloud-based systems, necessitate a meticulously crafted disaster recovery plan.
These shifts and the dynamic nature of technology require regular reviews and updates to your plans.
Increasing Costs
Three primary factors contribute to the costs associated with disaster recovery:
Data costs: Your data holds substantial value. Client records, invoices, projects, workflows, and databases are all at risk of being lost, which could potentially lead to severe financial repercussions for the company.
Cost of downtime: Any modern business relies a lot on electronic resources. So, once these resources go down, your business, partly or as a whole, cannot operate. This means that you will lose money with every hour of downtime.
Cost of additional resources & manpower: Lastly, if you are about to create a good disaster recovery plan for infrastructure of any complexity, you are going to spend both your time and your money. And, although the options for spending here are limitless, your budget isn’t. You will need more hardware, software, and workforce to develop, implement, and maintain a good disaster recovery solution.
Improper Disaster Recovery Processes
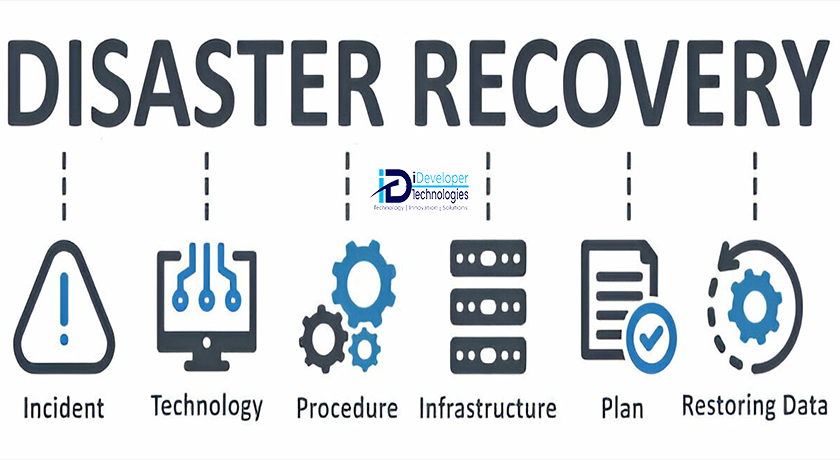
An inadequately structured disaster recovery strategy is as ineffective as having no strategy at all. To ensure a comprehensive disaster recovery workflow, concentrate on these four critical stages:
1. Planning: This stage is particularly challenging, as it requires you to establish your recovery time and recovery point objectives, devise the solution architecture, and choose appropriate vendors for both hardware and software.
2. Review: During this phase, collaborate with your technical team and executive leadership to evaluate your plan, ensuring that no critical elements have been overlooked and that the plan aligns with budgetary constraints.
3. Implementation: After completing the planning and review stages, proceed to implement the disaster recovery solution.
4. Regular tests and reviews: It is essential to conduct routine tests of your disaster recovery environment to confirm your readiness to restore workloads and data in various scenarios. Following these tests, reassess your plan and make necessary updates.
Insufficient Backup Protection
Even with the right processes established, the effectiveness of your tools is crucial. Assess whether all types of workloads are being adequately backed up.
For instance, if you utilize cloud virtual machines, you will require specialized tools and a tailored approach to ensure successful restoration of your architecture.
Additionally, it is risky to store all backup data in a single location. The widely accepted 3-2-1 backup strategy recommends maintaining at least three copies of each file, with two being backups and one stored offsite.
Finally, consider the significant risk posed by ransomware attacks, which are a prevalent threat to data security today. Ransomware can target both your files and backups, making adherence to the 3-2-1 rule essential for recovery capabilities, even in the event of an attack.
Hard to Meet the Regulatory Requirements
Your backup and disaster recovery policies are influenced by the industry in which your company functions. Various regulations exist, such as Data Protection laws in Kenya. These regulations outline specific requirements for data storage and protection. To avoid substantial penalties, it is essential to adhere to these compliance standards.
To sum up
A great backup and disaster recovery plan for SMEs, takes a good amount of effort, money, experience, and expertise. You should keep in mind all the details of your infrastructure, think of dozens of ways to lose your data, and then invent dozens of ways to recover it. All that should be a repeatable, carefully planned process. Sounds challenging, but it is also an absolute necessity for any SME in the modern world.